Wounds are an inevitable part of life, ranging from minor cuts and scrapes to more severe injuries requiring specialized care. Proper wound care is essential for promoting healing, preventing infections, and ensuring a smooth recovery process. Let’s explore the importance, techniques, and best practices for effective wound care:
Understanding Wounds
- Types of Wounds: Wounds vary in severity and type, including cuts, abrasions, punctures, burns, surgical incisions, and chronic wounds like ulcers.
- Wound Healing Process: The body’s natural healing process involves several stages – hemostasis, inflammation, proliferation, and remodeling – aiming to restore tissue integrity.
Importance of Wound Care
- Preventing Infections: Proper care minimizes the risk of infections, which can delay healing and lead to complications.
- Promoting Healing: Effective wound care supports the body’s natural healing process, facilitating quicker recovery and minimizing scarring.
Basic Steps in Wound Care
- Cleaning the Wound: Gently clean the wound with mild soap and water to remove debris or foreign particles. Avoid harsh scrubbing, which can further damage the tissue.
- Applying Antiseptics: For minor wounds, applying an antiseptic solution or antibiotic ointment can prevent infection.
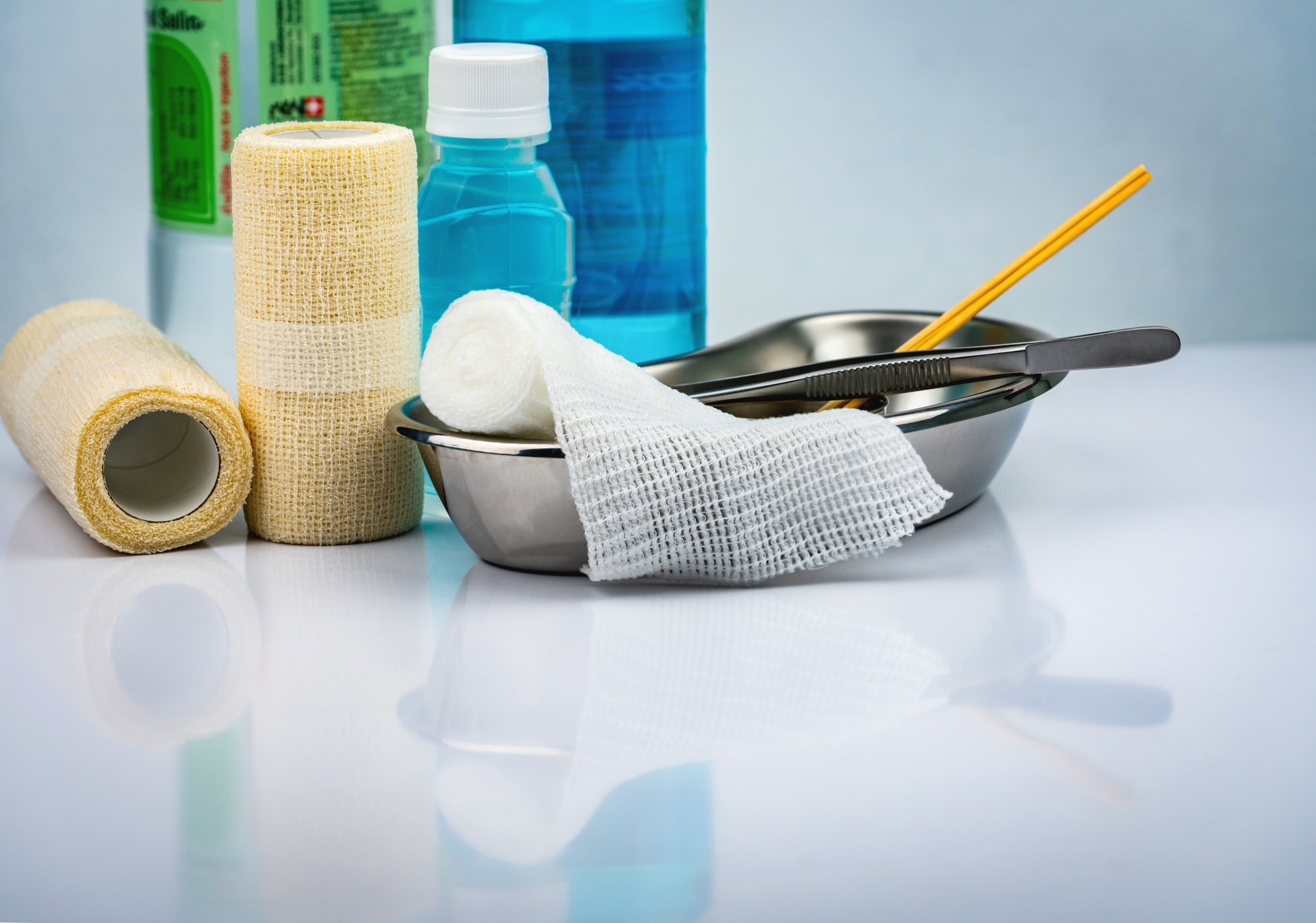
Dressings and Bandages
- Choosing the Right Dressing: Select dressings based on the type and severity of the wound. Options include gauze, hydrocolloid, hydrogel, foam, or transparent film dressings.
- Changing Dressings: Regularly change dressings as advised by healthcare professionals to maintain a clean and moist environment conducive to healing.
Advanced Wound Care
- Negative Pressure Wound Therapy (NPWT): NPWT uses a vacuum to promote healing in chronic or large wounds by removing excess fluid and promoting tissue growth.
- Debridement: Healthcare professionals may perform debridement to remove dead or infected tissue, facilitating faster healing.
When to Seek Medical Attention
- Signs of Infection: Watch for signs of infection like increased redness, swelling, warmth, pus, or worsening pain at the wound site.
- Slow Healing: Consult a healthcare provider if the wound doesn’t show signs of improvement or healing within a reasonable time.
Prevention and Long-Term Care
- Preventing Wounds: Taking precautions, such as wearing protective gear, using proper techniques during activities, and maintaining good hygiene, can help prevent wounds.
- Chronic Wound Management: Individuals with chronic wounds, such as pressure ulcers or diabetic foot ulcers, require specialized, ongoing care to prevent complications.
Conclusion
Proper wound care is crucial for facilitating the body’s natural healing processes and preventing complications. Whether it’s a minor cut or a more complex wound, adhering to the appropriate wound care techniques, seeking medical advice when necessary, and following through with prescribed treatments are vital steps toward achieving optimal healing and ensuring a smooth recovery journey. Effective wound care not only promotes physical healing but also contributes to the overall well-being and comfort of individuals on their path to recovery.